Help
This section will explain the parameters of four types of queries and how to interpret results.
Common Parameters.
Transcription Factor Somatic Motif.
RNA Binding Protein Somatic Motif.
miRNA Seed Somatic Motif.
miRNA-mRNA 3'UTR Somatic Motif.
Common Parameters
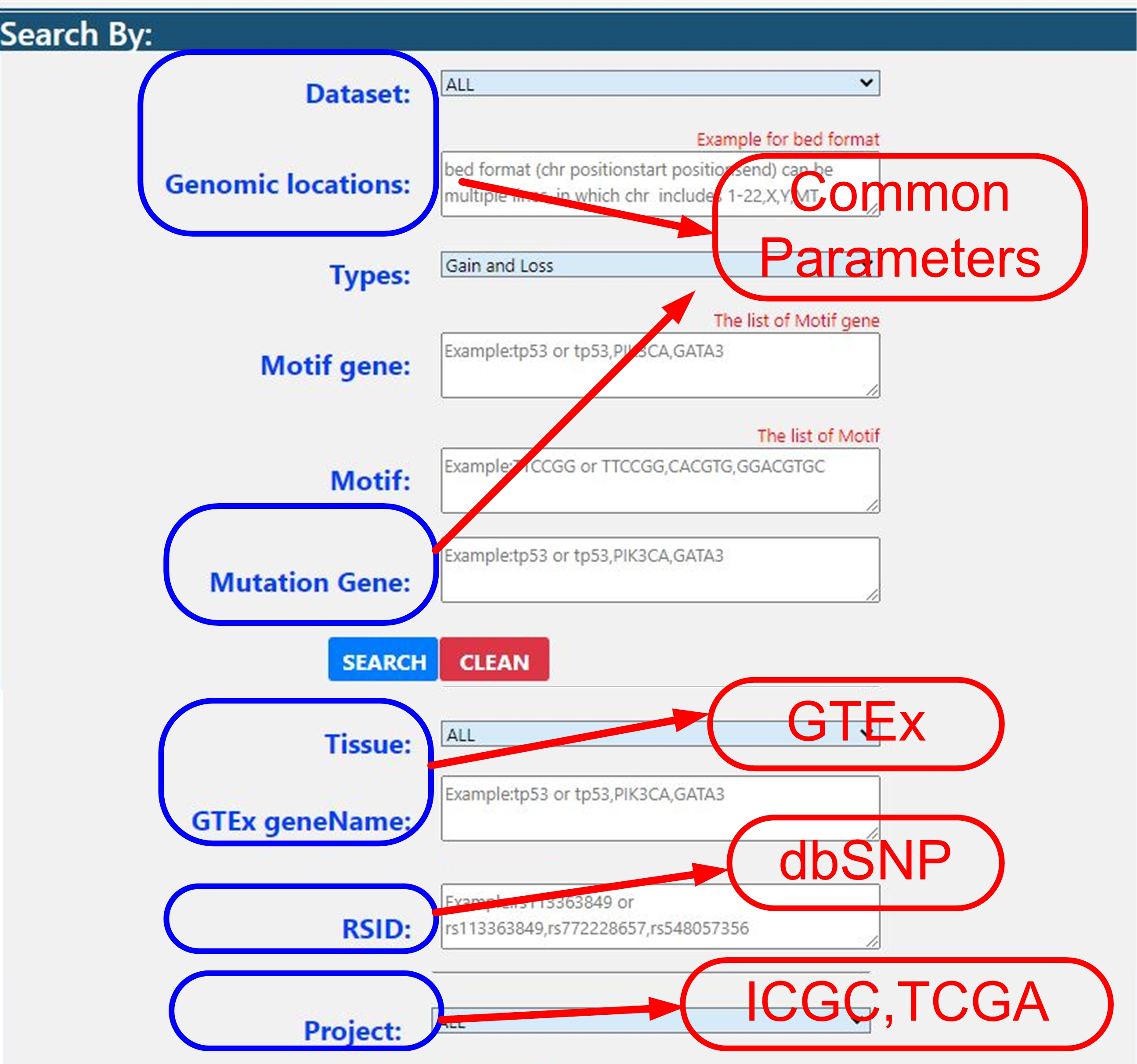
There are also four special parameters for four dataset:
| Parameters | Explanation |
| RSID | User can query by RS number on dbSNP data set. |
| Project | |
| Tissue and GTEx geneName | User can query by Tissue and cis-eQTL gene on GTEx data set. |
Transcription Factor Somatic Motif
1.Function:
Transcription Factors (TFs) usually bind to the promoter region of a gene. While the promoter is generally considered as a non-coding region, TF binding sites play critical roles in regulating gene transcription. We analyzed somatic mutations from three database to identify altered binding sequences for the 746 TF motifs extracted from JASPAR .
2.Parameters:
| Parameters | Explanation |
| Types | Sequence altering mechanisms can cause either gain or loss of important binding motifs . Therefore, users can query either or both gain and loss TFs binding motifs by this field. |
| Motif gene | Users can query data about TFs binding motifs gene by this field. Altered binding sequences for the 746 TF motifs extracted from JASPAR database. |
| Motif | This database includes 475 unique TFs motif sequences. Therefore, users can gain data about special TFs motif sequences by this field. For Example:TTCCGG or TTCCGG,CACGTG,GGACGTGC; To handle standard sequence ambiguities, mismatches, wild card or standard syntax for complex motif patterns, we set '_' character as wild card. For example:TT_CGG or TT_C_G. |
3.Interpretation of results:
Query Results
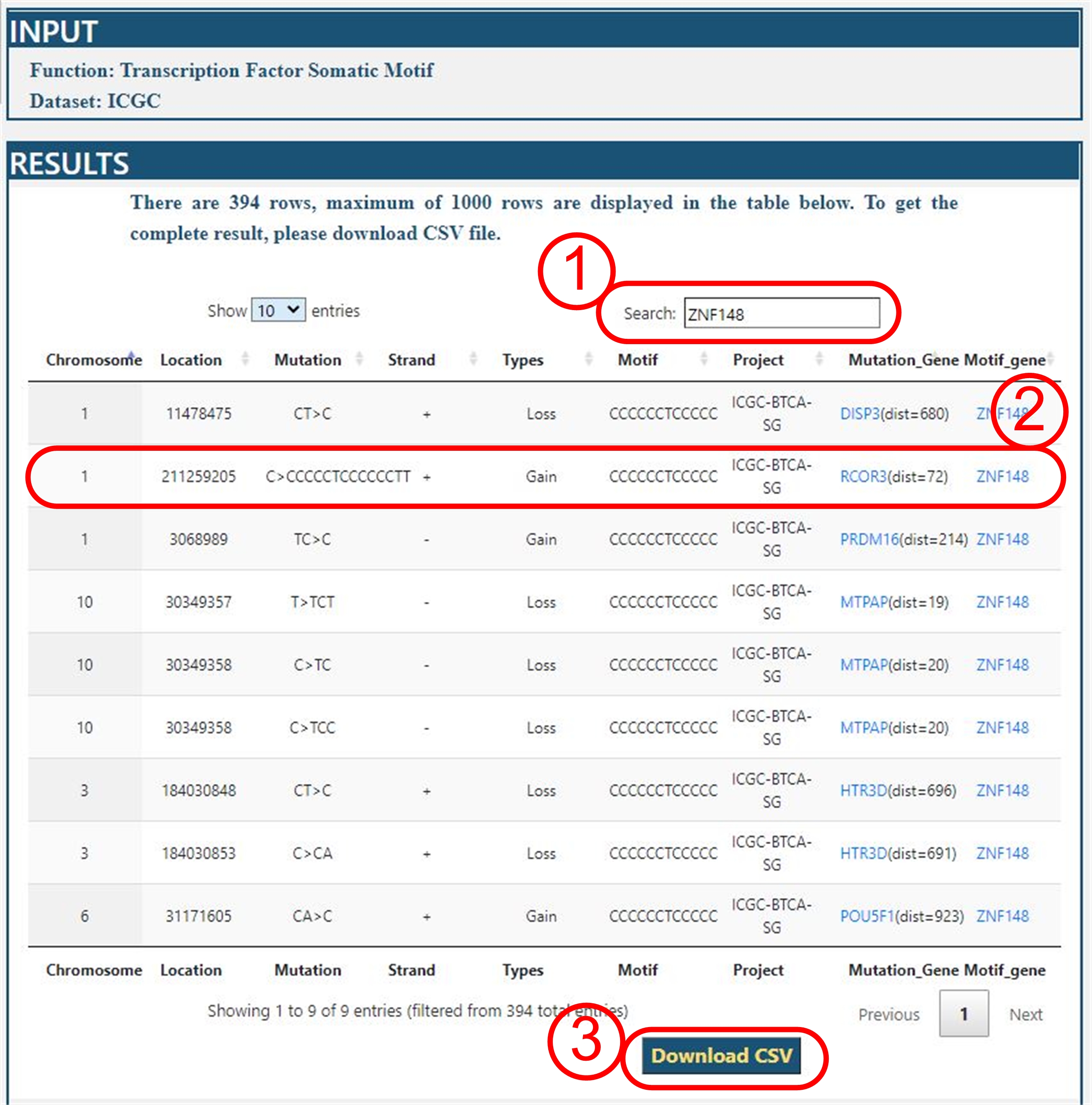
For example: we query all data of ICGC-BTCA-SG project on ICGC dataset.
The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) This section is Result table. But, this table display maximum of 1000
rows of all results. Here, we will interpret the result. For example,
in the BTCA-SG project, the mutation on position 211259205 of chromosome 1
of C>CCCCCTCCCCCCTT at the upstream of RCOR3 forms a new binding motif
sequence CCCCCCTCCCCC for ZNF148 gene. All mutation gene and motif gene
were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of gene.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
Query Results
For example: we query all data of ICGC-BTCA-SG project on ICGC dataset. The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) This section is Result table. But, this table display maximum of 1000
rows of all results. Here, we will interpret the result. For example,
in the BTCA-SG project, the mutation on position 211259205 of chromosome 1
of C>CCCCCTCCCCCCTT at the upstream of RCOR3 forms a new binding motif
sequence CCCCCCTCCCCC for ZNF148 gene. All mutation gene and motif gene
were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of gene.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
RNA Binding Protein Somatic Motif
1.Function:
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single-stranded RNA in cells through recognizing specific RNA recognition motifs. RBPs have been found to play important roles in the post-transcriptional gene regulation process, and their impact on cancer biology has been well documented. The primary RBP binding regions are 3’UTR and introns. We focused on RBP motifs using data in four major RBP databases (ATtRACT, ORNAment, RBPDB and RBPmap).
2.Parameters:
| Parameters | Explanation |
| Types | Sequence altering mechanisms can cause either gain or loss of important RBPs motifs. Therefore, users can query gain or loss RBPs motifs by this field. |
| Motif gene | Users can query data about TFs binding motifs gene by this field. Altered binding sequences for the 3,524 RBPs motifs extracted from four major RBP databases. User can download all result files about these 3,524 RBPs motifs. As the limitation of store space, user can query 58 important RBPs motifs in this database. |
| Motif | This database includes 58 unique RBPs sequences. Therefore, users can extract data about special RBPs sequences by this field. For Example:AATAAT or AATAAT,ATTGCAC,GCGGGCC. To handle standard sequence ambiguities, mismatches, wild card or standard syntax for complex motif patterns, we set '_' character as wild card. For example:AA_AAT or A_T_AT. |
3.Interpretation of results:
Query Results
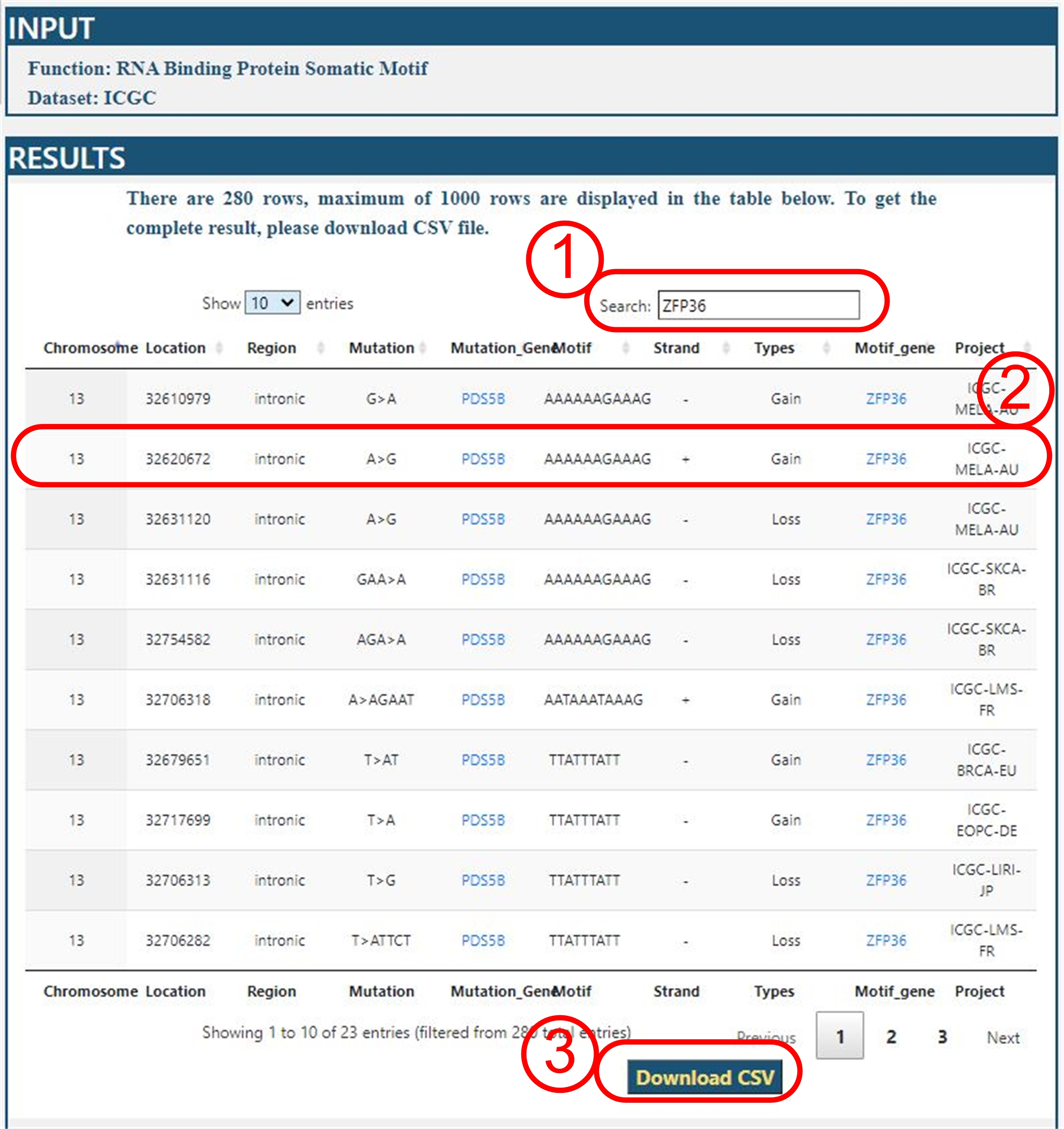
For example: we query all data of mutation gene POS5B on ICGC dataset.
The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) This section is Result table. But, this table display maximum of 1000
rows of all results. Here, we will interpret the result. For example,
in the MELA-AU project, the mutation on position 32620672 of chromosome 13
of A>G at the intronic of PDS5B forms a new binding motif
sequence AAAAAAGAAAG for ZFP36 gene. All mutation gene and motif gene
were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of gene.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
Query Results
For example: we query all data of mutation gene POS5B on ICGC dataset. The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) This section is Result table. But, this table display maximum of 1000
rows of all results. Here, we will interpret the result. For example,
in the MELA-AU project, the mutation on position 32620672 of chromosome 13
of A>G at the intronic of PDS5B forms a new binding motif
sequence AAAAAAGAAAG for ZFP36 gene. All mutation gene and motif gene
were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of gene.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
miRNA Seed Somatic Motif
1.Function:
miRNAs regulate mRNA through their seed sequences. With five databases (ICGC, TCGA, GTEx, REDIportal and dbSNP) somatic mutation data, we detect altered miRNA seeds.
2.Parameters:
| Parameters | Explanation |
| miRNAID | Users can applied miRNA number to query miRNA with mutational seeds. |
3.Interpretation of results:
Query Results
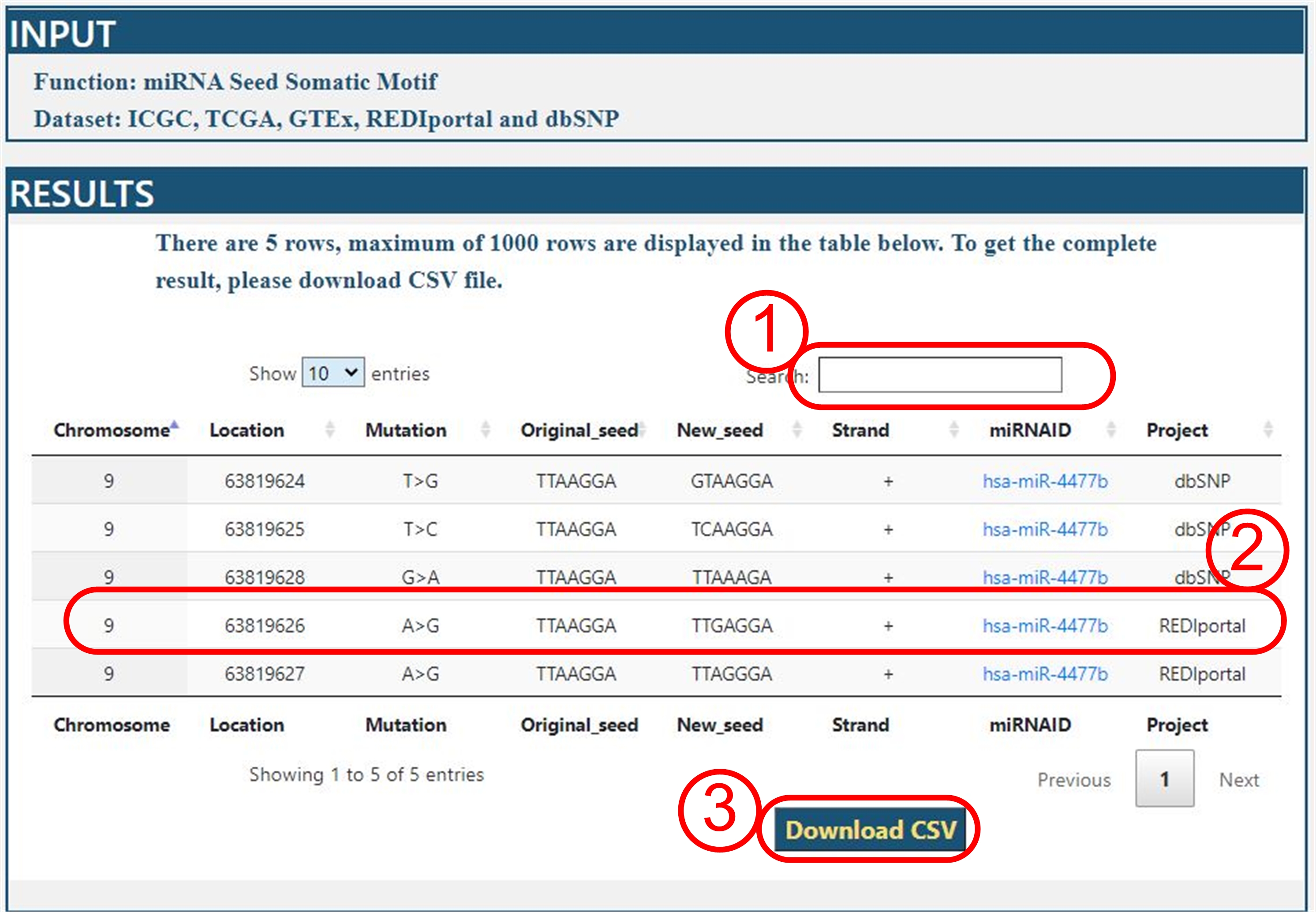
For example: we query all data of hsa-miR-4477b on five datasets.
The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) The A-to-I RNA editing event on position 63819626 of chromosome 9, caused hsa-miR-4477b seed TT[A]AGGA
to become TT[G]AGGA. All miRNA were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of miRNA.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
Query Results
For example: we query all data of hsa-miR-4477b on five datasets. The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) The A-to-I RNA editing event on position 63819626 of chromosome 9, caused hsa-miR-4477b seed TT[A]AGGA
to become TT[G]AGGA. All miRNA were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of miRNA.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
miRNA-mRNA 3'UTR Somatic Motif
1.Function:
miRNAs regulate mRNA through their seed sequences. Somatic mutations occurred in the seed regions can substantially alter the mRNA targets. Target mRNA 3’UTR binding sequences for the miRNA seeds were obtained from starBase 2.0. With five databases (ICGC, TCGA, GTEx, REDIportal and dbSNP) somatic mutation data, we detect altered miRNA targets.
2.Parameters:
| Parameters | Explanation |
| miRNAID | Users can applied miRNA number to query miRNA with mutational target gene. |
| Target gene | Users can applied gene name to query mutational target gene of miRNA. |
3.Interpretation of results:
Query Results
For example: we query all data of TP53 as target gene on five datasets.
The query result is as following:
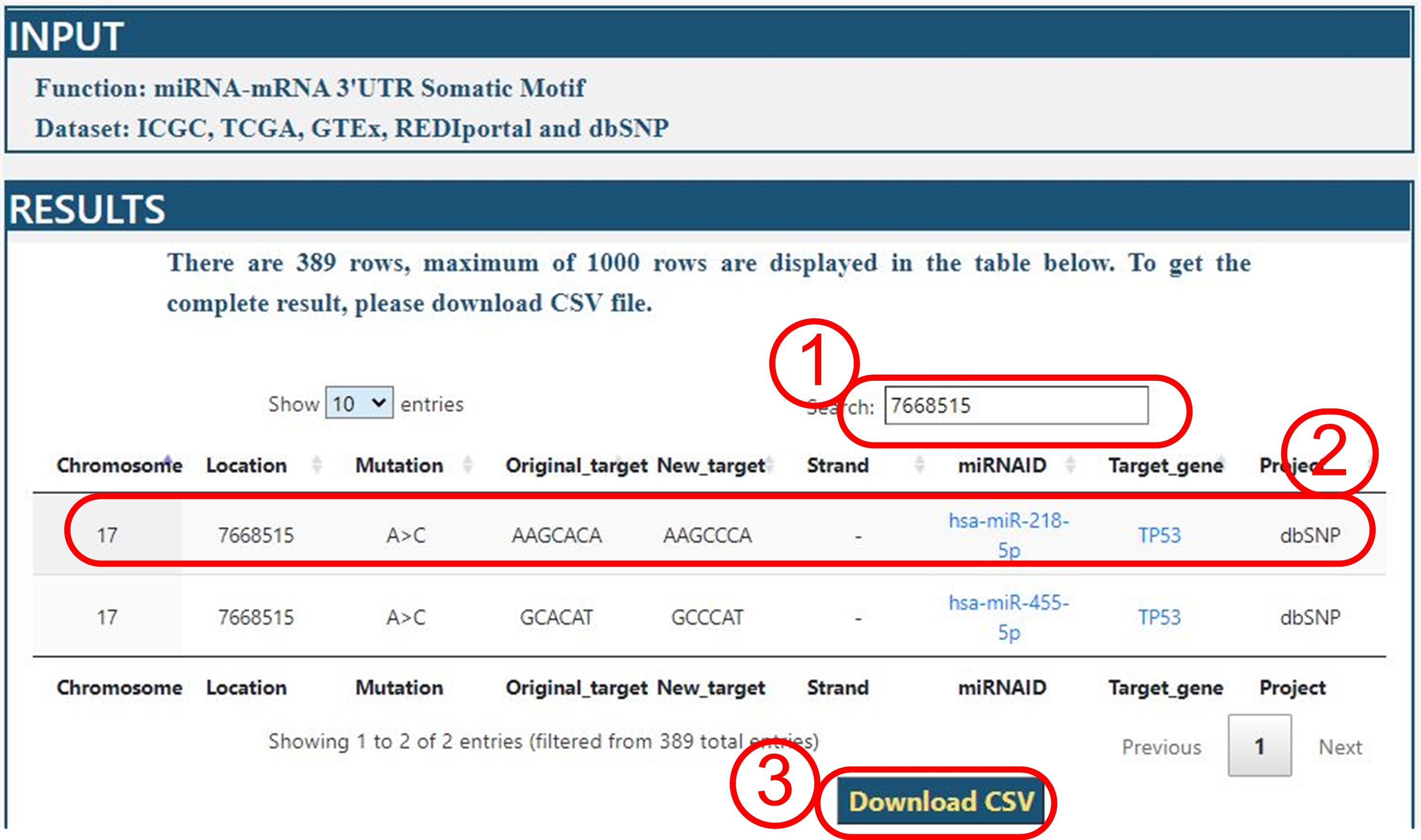
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) On dbSNP dataset, the mutation on position 7668515 of chromosome 17, caused the 3’UTR region of
TP53 from AAGC[A]CA to AAGC[C]CA, which is the target of miRNA hsa-miR-218-5p. All miRNA and target gene were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of miRNA and target gene.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.
Query Results
For example: we query all data of TP53 as target gene on five datasets. The query result is as following:
Interpretation
(1) User can search a key words in this field from query results.
(2) On dbSNP dataset, the mutation on position 7668515 of chromosome 17, caused the 3’UTR region of
TP53 from AAGC[A]CA to AAGC[C]CA, which is the target of miRNA hsa-miR-218-5p. All miRNA and target gene were linked to GeneCards database.
It is convenient to query the function of miRNA and target gene.
(3) All results can be downloaded in csv format for further analyses.