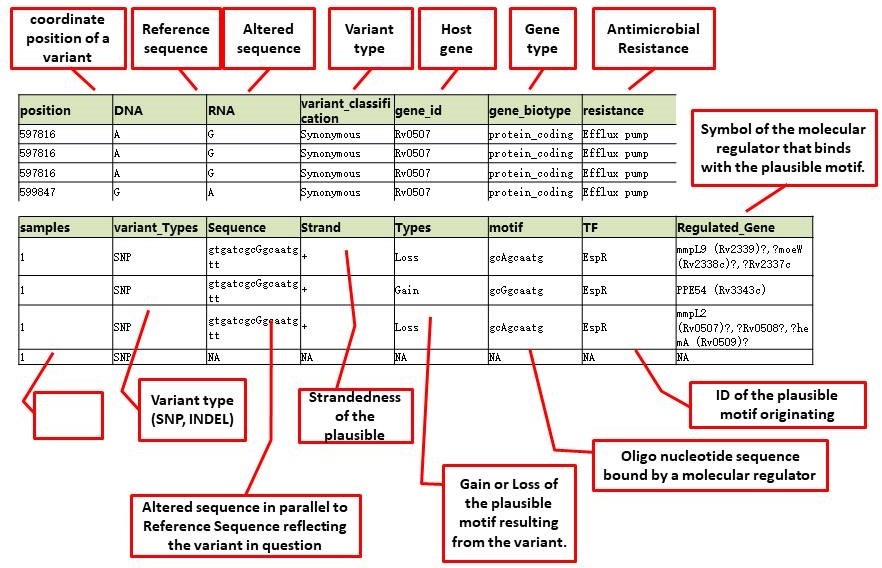
Introduction Query Explanation Citation
Introduction
RNA editing, while studied thoroughly in humans, has been sporatidally described in bacteria, and never reported in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb).
By comparing sequences from RNA and DNA from high-throughput sequencing data, we report the first finding of Mtb RNA editing in 32 clinical Mtb isolates,
and all RNA editing events were verified with a second RNA-seq experiment. The Mtb RNA editing type’s distributions are noticeably different from humans,
in which A-to-G RNA editing is the dominant type. Rather, C-to-T RNA editing was most abundantly identified in Mtb. In addition to point RNA editing,
indel RNA editing events were also detected. Further functional analyses showed that RNA editing events greatly affected transcription factor EspR’s binding sequences,
causing a cascading dysregulation effect on gene expression.
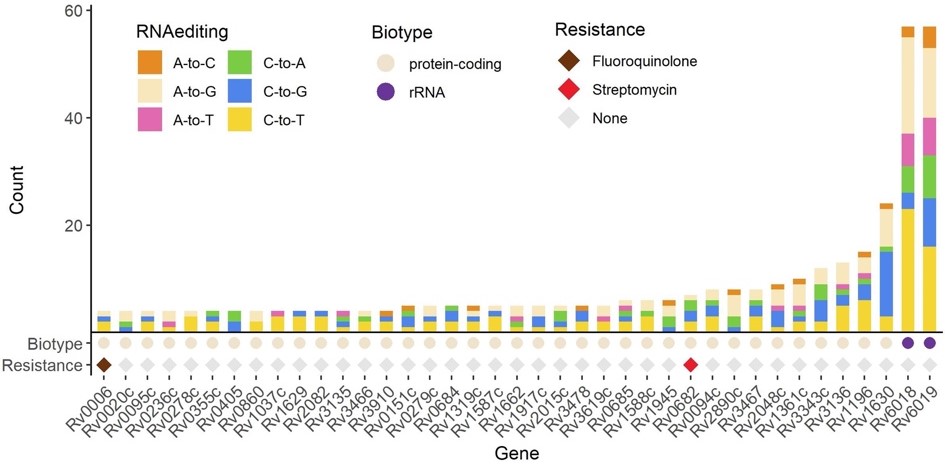
A bar plot describes RNA editing events by gene, gene’s biotype, and known association with drug resistance. This bar plot is limited to genes with at least four RNA editing positions.
Citation
Contact
We appreciate your comments to make our website more complete in the future, please contact:
Yan Guo, Ph.D, Yaguo@salud.unm.edu
Limin Jiang, M.S., jianglm@tju.edu.cn